What is education?
Education is a systematic process of acquiring knowledge, skills, values, beliefs, and habits. It involves the imparting and receiving of information through various mediums such as teaching, training, storytelling, discussion, and research. Education can occur in formal settings like schools, colleges, and universities, as well as in informal settings like homes, communities, and workplaces.
The goals of education typically include the development of cognitive abilities, critical thinking skills, problem-solving skills, socialization, cultural awareness, personal growth, and preparation for future roles in society. Education plays a crucial role in shaping individuals and societies, empowering people to contribute meaningfully to their communities, economies, and the world at large. It encompasses a broad range of disciplines and subjects, catering to diverse interests, talents, and aspirations.
- Types of Education: Education can be broadly categorized into formal, informal, and non-formal education.
- Formal Education: Structured education is typically provided in schools, colleges, and universities, following a prescribed curriculum and leading to recognized qualifications or certifications.
- Informal education is learning that occurs through daily life experiences, interactions with others, observation, and self-directed study outside of formal educational institutions.
- Non-formal education: structured learning that does not necessarily lead to formal qualifications, often focused on specific skills or knowledge areas. Examples include workshops, vocational training, and community-based programs.
- Stages of Education: Education is typically divided into stages, such as early childhood education, primary education, secondary education, and higher education. Each stage builds upon the previous one and serves different developmental needs and objectives.
- Curriculum: The curriculum is a set of courses, subjects, and learning activities designed to achieve specific educational goals. It outlines what students are expected to learn and guides the teaching and learning process.
- Educational Systems: Different countries have varying educational systems, structures, and policies influenced by cultural, social, economic, and political factors. These systems may prioritize different aspects of education, such as academic excellence, vocational training, or holistic development.
- Technology in Education: Technology has increasingly become integrated into education, transforming how learning materials are delivered, accessed, and consumed. Digital tools, online platforms, educational software, and multimedia resources enhance teaching effectiveness, student engagement, and accessibility to education.
- Lifelong Learning: Education is not confined to formal schooling but is a lifelong process of acquiring knowledge, skills, and competencies throughout one’s life. Lifelong learning is essential for personal and professional development, adaptation to changing circumstances, and staying relevant in a rapidly evolving world.
- Role of Educators: Educators play a critical role in facilitating learning and providing guidance, mentorship, and support to students. Effective educators foster a positive learning environment, encourage critical thinking, creativity, and curiosity, and adapt teaching methods to meet the diverse needs of learners.
Overall, education is fundamental to individual empowerment, societal progress, and the advancement of civilization. It equips individuals with the tools and capabilities to navigate the complexities of the world, pursue their aspirations, and contribute to the betterment of society.
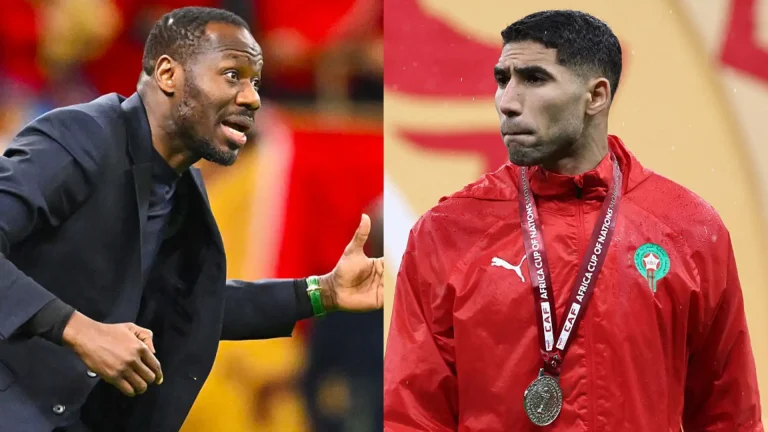
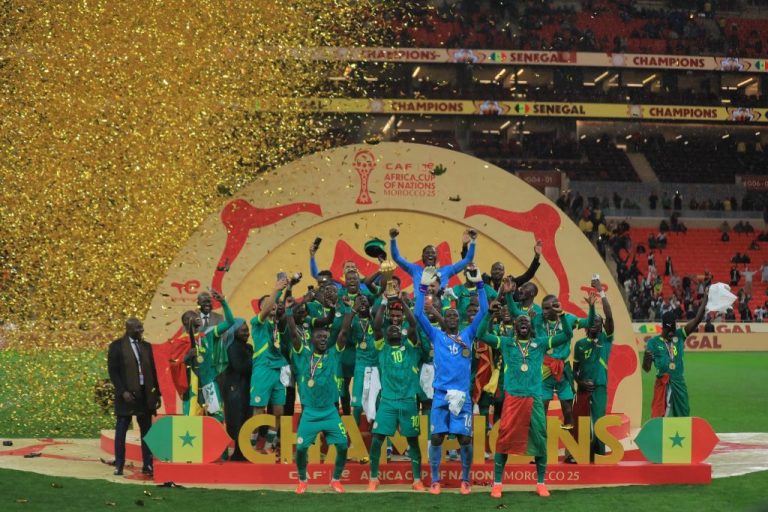
- Senegal boss & Achraf Hakimi slapped with bans and over £1m in fines handed out to AFCON champions and Morocco after final chaos
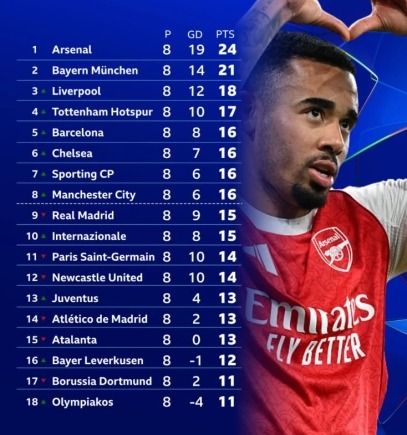
- List of the qualified teams for the next round of the UEFA Champions League
- Senegal officially crowned AFCON winners as CAF slams both finalists with unprecedented sanctions
- Slim Buster: “Don’t rely on women to fund your music career,” he tells emerging artists.
- CAF bans Senegal coach Pape Thiaw for 5 matches, fines him $100K.